We have access to a common pool of computer resources in the cloud (Servers, storage, applications, and so on) when we use cloud computing. You just need to request extra resources as needed. Continue reading as we discuss the various types of cloud deployment models and service models to assist you in determining the best option for your company.

What is a cloud deployment model?
A cloud deployment model denotes a specific cloud environment depending on who controls security, who has access to resources, and whether they are shared or dedicated. The cloud deployment model explains how your cloud architecture will appear, how much you may adjust, and whether or not you will receive services (Patel and Kansara, 2021). The links between the infrastructure and your users are also represented by types of cloud deployment models. Because each type of cloud deployment model may satisfy different organisational goals, you should choose the model that best suits the approach of your institution.
Different Types of Cloud Deployment Models
The cloud deployment model specifies the sort of cloud environment based on ownership, scalability, and access, as well as the nature and purpose of the cloud (Gupta, Gupta and Shankar, 2021). It defines the location of the servers you’re using and who owns them. The cloud deployment model describes the appearance of your cloud infrastructure, what you may alter, and whether you will be provided with services or must design everything yourself.
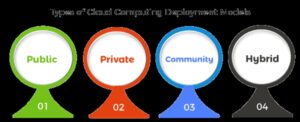
Types of cloud deployment models are:
Public Cloud Deployment
Anyone may use the public cloud to access systems and services. Because it is exposed to everybody, the public cloud may be less secure. The public cloud is one in which cloud infrastructure services are made available to the general public or significant industrial organisations over the internet. In this deployment model, the infrastructure is controlled by the organisation that provides the cloud services, not by the user.
Private Cloud Deployment
The private cloud deployment approach is opposed to that of the public cloud. It is a one-on-one setting for a single user (customer). It is not necessary to share your hardware with anyone. The contrast between private and public clouds is in how all of the hardware is handled. In this deployment model of cloud computing, the cloud platform is deployed in a secure cloud environment secured by robust firewalls and overseen by an organization’s IT staff.
Hybrid Cloud Deployment
Hybrid cloud deployment provides the best of both worlds by linking the public and private worlds with a layer of proprietary software. With hybrid cloud deployment, you may host the app in a secure environment while benefiting from the cost benefits of the public cloud. In this, organisations can migrate data and applications between clouds by combining two or more cloud deployment strategies. The hybrid cloud deployment is also popular for ‘cloud bursting.’ It means that if a company operates an application on-premises, but it experiences a high load, it might explode onto the public cloud.
Community Cloud Deployment
It enables a collection of businesses to access systems and services. It is a distributed system formed by combining the services of many clouds to meet the special demands of a community, industry, or enterprise. The community’s infrastructure might be shared by organisations with similar interests or duties. In this deployment model of cloud computing, cloud deployment is often handled by a third party or a collaboration of one or more community organisations.
Cloud Computing Service Models
Cloud computing enables the delivery of a variety of services defined by roles, service providers, and user firms. The following are major categories of cloud deployment models and services:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS refers to the employment and use of a third-party provider’s IT Physical Infrastructure (network, storage, and servers) (Malla and Christensen, 2019). Users can access IT resources via an internet connection because they are hosted on external servers.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides for the outsourcing of physical infrastructure as well as the software environment, which includes databases, integration layers, runtimes, and other components.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is delivered through the internet and does not require any prior installation. The services are available from anywhere in the world for a low monthly charge.
Conclusion
Over time, the cloud has changed drastically. It was initially only an unusual choice with a few modifications. It is available in a variety of flavours, and you can even establish your Private cloud deployment or Hybrid Cloud deployment in your data centre. Each deployment model of cloud computing offers a unique offering that may considerably boost your company’s worth. You may also change your Cloud deployment model as your needs change.