5G and edge computing are creating plenty of new income opportunities in industries like manufacturing, transportation, and gaming. How can communication service providers acquire a competitive advantage? Everything you need to know is provided here.

What is Telco Edge?
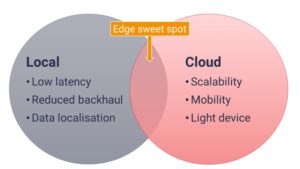
Telecommunications companies frequently associate edge computing with mobile edge computing or multi-access edge computing – computing at the network’s edge. Telco edge computing, on the other hand, comprises workloads operating on client-premises equipment and other points of presence at the customer site. The term “telco edge” refers to distributed computation maintained by the operator that may extend beyond the network edge and onto the customer edge. Telco Edge combines the advantages of both local and cloud computing. Telco edge computing should be adaptable and scalable. Telco edge computing can handle unexpected surges in workloads caused by increased end-user activity or answer organizations’ need to grow fast while building, testing, and deploying new applications (Klas, 2017).
What exactly is Telco Edge Cloud (TEC)?
The Telco Edge Cloud is a worldwide platform solution for exposing, managing, and marketing Edge Computing, Network resources, and capabilities across multiple operators and national borders, utilising existing and future network assets. Telco Edge Cloud is building a platform built on open technologies and telecom standards. MNOs may monetize their edge resources thanks to Telco Edge Cloud.
The Telco Edge Cloud idea and architecture are beneficial not only to MNOs but may also be utilised by other service and edge providers to improve their services since capabilities like NaaS are made available to these third parties (Baliosian et al., 2021). Other edge and cloud providers can give methods to their application development communities to optimise edge application performance and experience by consuming Telco Edge Cloud NaaS capabilities and implementing them into their platform offerings.
Telco Edge Computing
Telco Edge computing is also known as Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) or Multi-Access Edge Computing (MAEC). Telco Edge computing provides execution resources for applications that need networking close to end users, often within or near the operator network’s boundary (Gebhardt et al., 2012).
Telco Edge computing may also be installed on corporate premises. Communication service providers or service providers can manage or host the edge infrastructure. Several use cases necessitate the deployment of distinct apps at multiple locations. In such cases, a distributed cloud may be viewed as an execution environment for applications spread over numerous sites, with connections maintained as a single solution. The key advantages of Telco Edge computing are low latency, high bandwidth, device processing, and data offload, and trusted computing and storage.
What is a 5G Telco Cloud?
A 5G Telco Cloud is a software-based cloud architecture that allows for the placement of 5G network functions/applications and the division of a single infrastructure into various network slices for the delivery of a wide variety of services ranging from eMBB to URLLC (Gebremariam et al., 2021). It enables you to swiftly add services, respond fast, and manage resources efficiently and automatically.
Network function virtualization, software-defined networks (SDN), edge computing, and microservices are components of 5G Telco Cloud.
1. Network Functions Virtualization of 5G Telco Cloud enables you to abstract operations from hardware. This enables conventional servers to execute operations that would otherwise necessitate the utilization of hardware.
2. Software-Defined networking (SDN), a new backhaul/mid-haul design of 5G Telco Cloud, is adaptive, manageable, and versatile. It is perfect for the fluidity of 5G applications. This design isolates network control from forwarding services, allowing network control to be programmed directly.
3. Microservices are a method of separating applications and network operations into loosely linked systems. DevOps cycles or CI/CD can be used to manage them.
5g and Edge computing
5G and edge computing are intricately related technologies: both are set to greatly increase application performance and enable massive volumes of data to be handled in real-time. 5G speeds can be up to 10 times faster than 4G, while mobile edge computing minimises latency by putting computational capabilities closer to the end user.
5G and edge computing are technologies that can work together to power a new generation of smart devices and apps. 5G’s enhanced performance can improve edge computing applications by lowering latency, improving application response times, and enhancing organizations’ capacity to gather and analyze data.
Benefits of the Relationship between 5G and Edge Computing
1.
Ultra-low latency use cases: The combination of 5G with edge computing is important for achieving ultra-low latency in a variety of edge devices and use cases.
2.
Near real-time performance: Using 5G and edge computing together allows organizations to collect and process large amounts of real-time data to optimize various operational processes and increase productivity and customer experiences.
3.
Improved bandwidth usage: The connection between 5G and edge computing influences the success of 5G network technologies.